Introduction to Drip Water System
A drip water system is an effective and affordable method for watering yards, nurseries, and agricultural fields. It is widely used in dry regions where water conservation is essential. Compared to other irrigation methods such as sprinklers, which operate at 65–75% efficiency, drip irrigation achieves nearly 90% efficiency by delivering water directly to plant roots.
Drip irrigation reduces evaporation and runoff while applying water slowly and precisely where it is needed most. Although it has traditionally been used in farms and nurseries, homeowners are now increasingly adopting drip irrigation due to rising water costs and sustainability concerns.
Need for Water-Saving Irrigation Solutions
As water costs continue to rise in dry regions, farmers are actively seeking ways to reduce water usage and prevent wastage. Efficient irrigation tools help farmers save money, improve crop health, and make better use of limited water resources.
Below are five important tools commonly used by farmers to optimize irrigation and conserve water.
Drip Irrigation Systems
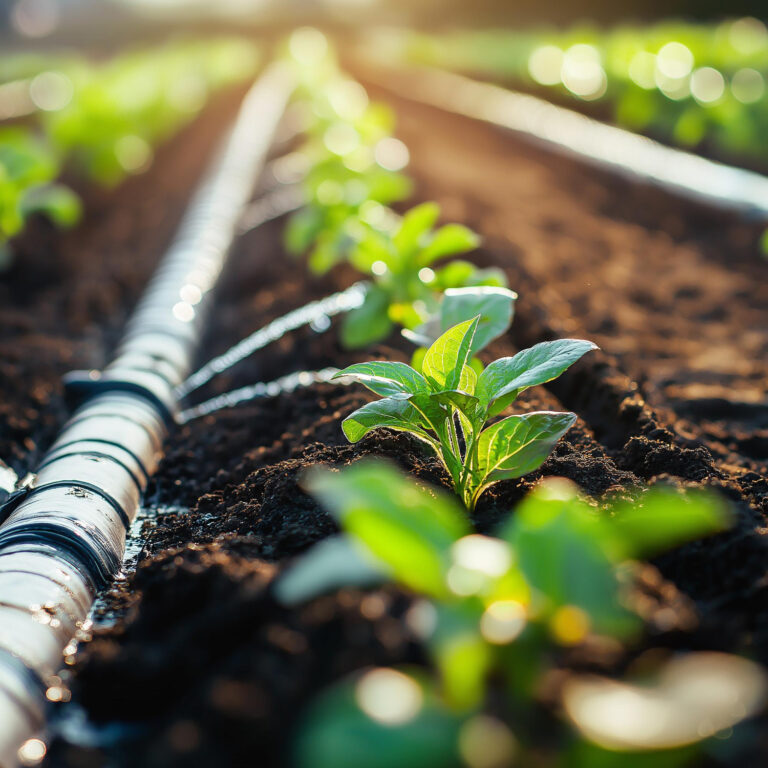
Drip irrigation is one of the most efficient methods of delivering water to crops with minimal waste. Although currently used on less than 2% of agricultural land worldwide, it can reduce water consumption by 30% to 70%.
Despite the higher initial installation cost, drip irrigation offers several long-term benefits such as reduced evaporation, minimized weed growth, and precise water delivery to crop root zones.
Water Flow Meters
Water flow meters accurately measure the amount of water used for irrigation. They help farmers monitor water consumption, avoid over-irrigation, and calculate the exact volume of water used during a specific period.
Monitoring flow rates also helps identify system issues such as leaks or blockages, making water flow meters an essential irrigation management tool.
Soil Sensors
Soil sensors measure soil properties such as moisture levels, enabling farmers to determine the precise amount of water required by crops. Advanced precision agriculture systems integrate soil sensors with digital devices to adjust water flow in real time.
These sensors help prevent over-watering, nutrient leaching, shallow root development, and unnecessary water wastage.
Irrigation Management Mobile Applications
Irrigation management mobile applications allow farmers to monitor and control irrigation systems remotely. These apps enable quick adjustments to watering schedules based on weather changes and crop needs.
Smart irrigation apps use weather data from nearby stations to guide farmers on how much water crops require, improving efficiency and conserving water.
Use of Drones in Irrigation
Drones are becoming increasingly important in modern agriculture. Equipped with thermal cameras, drones can detect irrigation leaks and identify areas receiving too much or too little water.
This technology allows farmers to improve irrigation accuracy, reduce water loss, and enhance crop health, especially on large farms.
System Components and Design
A drip water system consists of several essential components including:
- Main line
- Sub-main
- Valves
- Filters
- Pressure regulators
- Backflow preventers
- Drip tubing
- Emitters
- Fittings and end caps
The mainline connects the water source to the valve, while the sub-main distributes water to drip tubing. The combined length of the mainline and sub-main should not exceed 400 feet.
Valves, Filters, and Pressure Regulation
Valves control water flow and can be operated manually or automatically. Backflow preventers ensure irrigation water does not contaminate the main water supply.
Pressure regulators are required if water pressure exceeds 40 PSI. Filters with at least a 150-mesh screen are recommended to prevent emitter clogging.
Drip Tubing and Emitters
Drip tubing is typically made of polyethylene and contains emitters that release water at a controlled rate. Tubing lengths should not exceed 200 feet from the water entry point.
Tubing should be secured with stakes and generally not buried to avoid clogging and rodent damage.
Emitter Design and Spacing
Emitters may be evenly spaced for row crops or placed at intervals for trees and shrubs. Emitter hoses usually have emitters spaced about 18 inches apart.
Trees and bushes typically require two emitters per plant. Emitters commonly release 1 gallon per hour, though ½ gallon per hour emitters are often more efficient.
Advantages of Drip Water System
- Reduces water contact with leaves, minimizing plant diseases
- Keeps spaces between rows dry, reducing weed growth
- Saves water, time, and money
- Reduces labor requirements
- Improves efficiency on uneven land
- Prevents nutrient leaching below the root zone
Conclusion
Drip irrigation is a highly efficient and sustainable watering solution for agriculture and landscaping. By delivering water directly to plant roots and minimizing wastage, it improves crop yield while conserving valuable water resources. When combined with modern technologies such as sensors, mobile apps, and drones, drip irrigation becomes an essential system for sustainable farming.